Audio and Video
Provide text for audio content
Audible content is inaccessible to users who are deaf or hard of hearing. Other users may be unable to access audio for environmental reasons—for example, because they are accessing the Web in a public space, or using a device such as a handheld or cell phone that does not support audio output. To make audio accessible, the equivalent content must be available as text.
Audio content comes in various forms—from music to sound to spoken narration and dialogue. While words cannot represent music or sound, words can describe them. Captions, for example, often describe sounds such as glass breaking or a car door slamming. On the other hand, spoken audio can be effectively represented as text. For example, a text transcript of a lecture or speech has the equivalent information contained in the audio presentation. When providing access to spoken audio, provide a text version along with the audio file. With both the audio file and transcript readily available, users can choose to read, listen, or both (Figure 12.1).
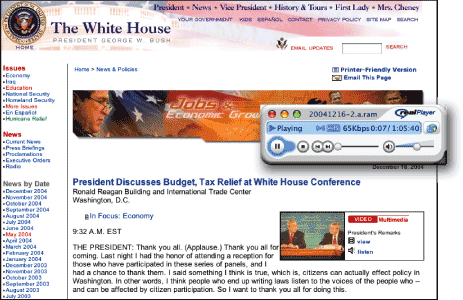
Figure 12.1: The White House site contains an extensive collection of speech transcripts, some with accompanying audio files and some with video. When spoken information is presented with a transcript, users can access the information by listening, reading, or both. www.whitehouse.gov
When audio is part of a video presentation, a text transcript alone will not suffice. Users who cannot hear need access to the information contained in the audio while viewing the video. In this case, synchronize the text with the video by using captions (Figure 12.2).
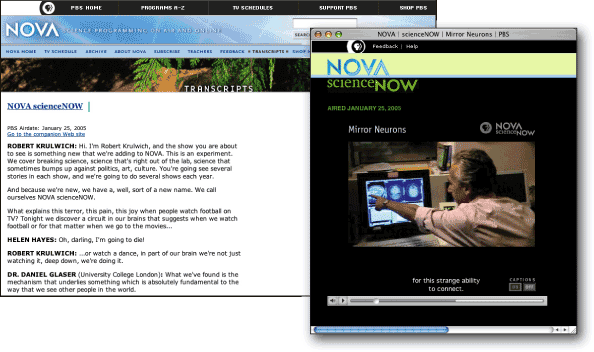
Figure 12.2: The Nova site is exemplary in providing captioned videos. Here, users can choose to view the video with or without captions. Users can also access the audio portion of the video via a text transcript. www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow
When providing access to audio via synchronized captions, a separate page containing the text transcript may be useful to users who cannot access the video—for example, because they do not have the correct plugin or are connecting to the Internet using a slow modem. Also, some users may prefer to access the transcript alone, perhaps for printing and review. Additionally, a text transcript improves search engine indexing.

